Opportunity
Africa is among the fastest-growing consumer markets in the world, hence making the retail sector one of the most prominent business sectors in Africa. An increase in opulence, population growth, the rate of urbanization, and an increase in the percentage of people who have access to the internet on the continent present exciting opportunities for expansion in the retail sector. Furthermore, the amount of money generated from customer expenditure has grown at a compounded rate of 3.9% since 2010 and is expected to reach 2.1 trillion by 2025 if the right systems are implemented.
On the downside, the majority of the retail transactions take place in informal, roadside markets where daily tasks are performed and recorded manually, resulting in poor management funds, unaccountability, mistrust among workers, and generally reducing the efficiency of the businesses but also proving an enormous potential for entrepreneurial actions that will cause a shift from traditional retail methods to incorporating modern technology in the retail sector.
In the open marketplaces in cities and villages throughout Africa, women traders usually predominate. This gives women considerable weight as economic actors because these marketplace systems are the primary distributive networks in most parts of Africa. Many of Africa’s consumer goods and foodstuffs move through their intricate chains of intermediaries, including market retailers, neighborhood shops, street vendors, wholesalers, and travelers who collect goods from farms, factories, and ports.
To further understand the market, I undertook a month-long of ethnographic research using observational shadowing and in-person interviews with over 200 participants across Accra.
Research findings

- Reason for opening a retail outlet
–Some retailers opened other stores like cosmetic stores before switching to retail of provisions and drinks because they heard it is very profitable
-Others entered the retail sector because of passion and the need to take care of their families
- Difficulties in running a retail shop
- Stocks (restocking and management)
- Some retail shop owners struggle with contacting the suppliers of the products, which run out quickly, and would have to do without them for a while, causing them to lose revenue.
- Some forget which products should be bought when restocking
- Most cannot tell what products have expired
- Prices change in the market whenever they go to restock their inventory
- Some products barely sell at all until they expire
- Stocks (restocking and management)
- RevenueMost retailers do not know the amount of profit they make from their sales. There is very vague knowledge of the cash flow of the business
- TrustGiving out too little change or too much change to customers due to mistakes made when calculating change due to be given to the customer some retail shop owners fear that their attendants might steal money and products when they are not around
- Rush hours
- Lots of people visit stores in the morning and evening, especially when people are going to work and coming back from work or school.
- Rush hours
- Tools being used or considered
- Laptop and an offline application to record sales and profits
- Laptops for making and managing mobile money transactions
- CCTV cameras are used to monitor all shop activities
- Main features that should be focused on
- Some retailers need a way to tell which products are in and out of stock
- The ability to view the profit they are making while comparing it to previous items
- Being able to manage and view store activity remotely
- Expiry dates of products
- Display fast-moving products and slow-selling products
- Checking for theft
- Some count the amount of money made and then verifies if it tallies with the products sold.
- Characteristics of the stores
- Most divide their money into two or three sections based on their sales.
- Some have a wholesale outlet and sell small provisions. Some run mobile money outlets as well.
- Some stores allow customers to pick up their products while others pick up the products for them
- Some have attendants; some have their family members, especially kids helping out.
- Some owners are the same ones who must take care of all aspects of the shop all by themselves.
- Some sell products individually, and others sell in packs(wholesale)
- if some retailers have to go to the market or leave the store, she leaves only trustworthy people in charge and not strangers because of theft.
- All containers pay fixed amounts of money for tax, which is not based on how much the store makes.
- Most retailers count the amount of money made at the end of the day
- Some of the money from sales is used by retailers to fend for themselves and their families and add new stocks
- Most retailers bring their back sales from the previous day to cater for expenses incurred when purchasing new stock or others.
- Some retailers sell products on credit
- Retail shop owners differentiate products by their price and not by their size
- Some products like bread, pure water, airtime, mobile money profits, etc. are not recorded on the application.
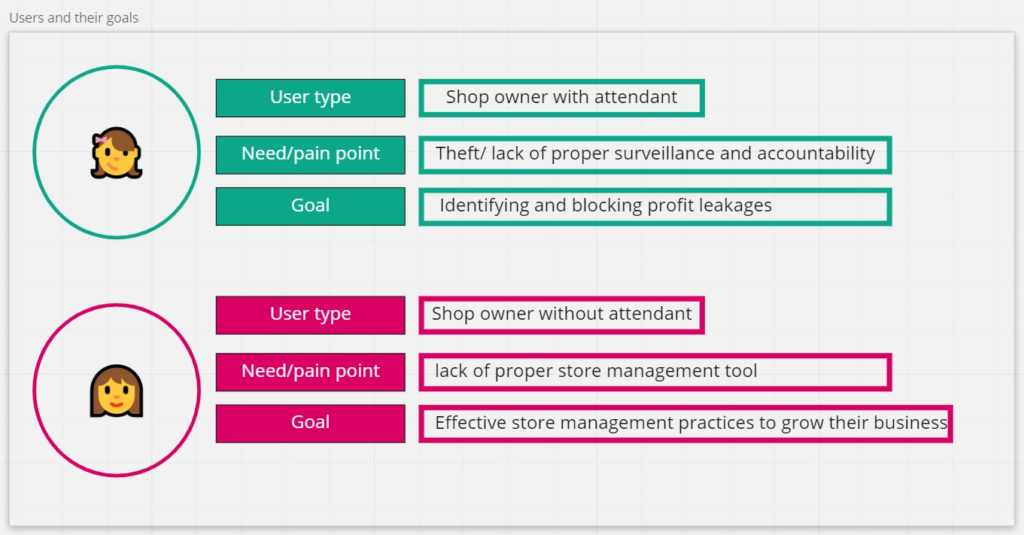
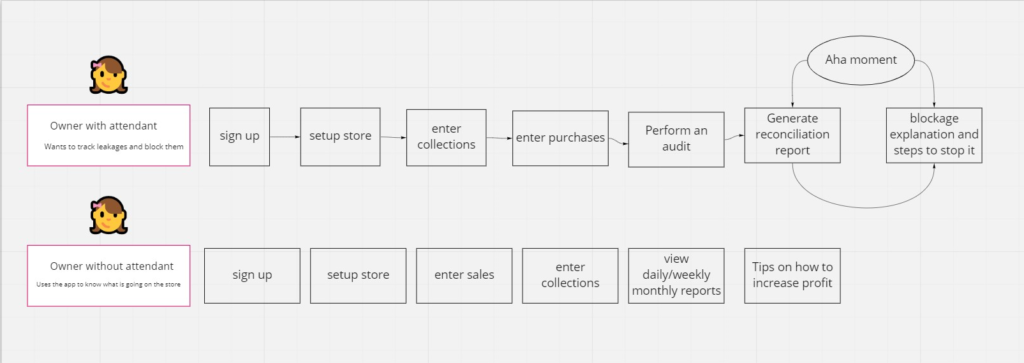
User Personas
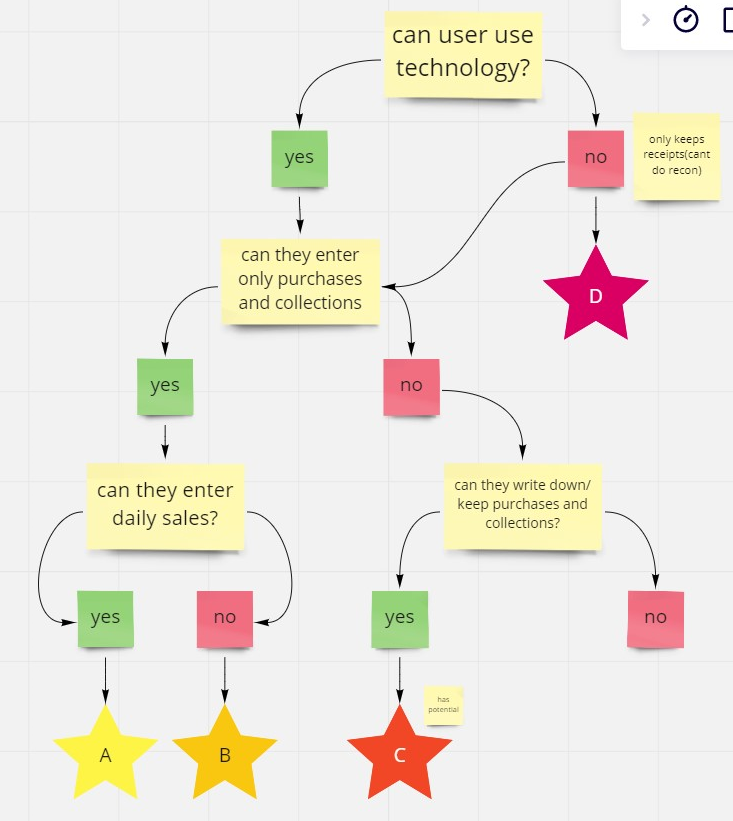
Use cases
List of requirements
- Profitability: showing how much profit the business is making
- Contacting suppliers for replenishment of stocks
- Shopping list to keep a list of items to buy from open markets.
- Alerting which products are out of stock
- Alert which products have expired
- Showing entire cashflow
- Change calculator – Itemized bill + Receipt generator
Trust
- Check-in on an attendant – Constant notification of sales remotely
- Activity log – knowing every activity done by the attendant
- End-of-day sales
- Audit (count the number of items in the shop and cross-check with a number on the app)
- Allow both attendants n owners to view audits
Speed
- Speed inputting of data during rush hour-voice record function
- Use bar code to record products sold
- Offline application
Restocking
- Show fast-moving products
- Show cheapest products
- Loan facility with very insignificant interest
Sales
- Selling products in packs (wholesale mode)
- Selling products individually (retail mode)
- Device set aside specifically for running the application
- Get a phone and pay in installments
- Show the average price of how products are being sold so they do not underprice or overprice
- Allows retailers to input money received from sales of products that are not on the application’s database
- Allow for different logins for each category of user ie owner, attendant, family member, etc
- Display the price of products when it is being searched for
- Allow retailers to add that a product was sold on credit and indicate when the money will be paid
- Allow retailers to enter the amount of money taken out of sales
- Allow distributors to know when to restock products in a shop automatically
- Restrict access to some modules based on role
Wireframes


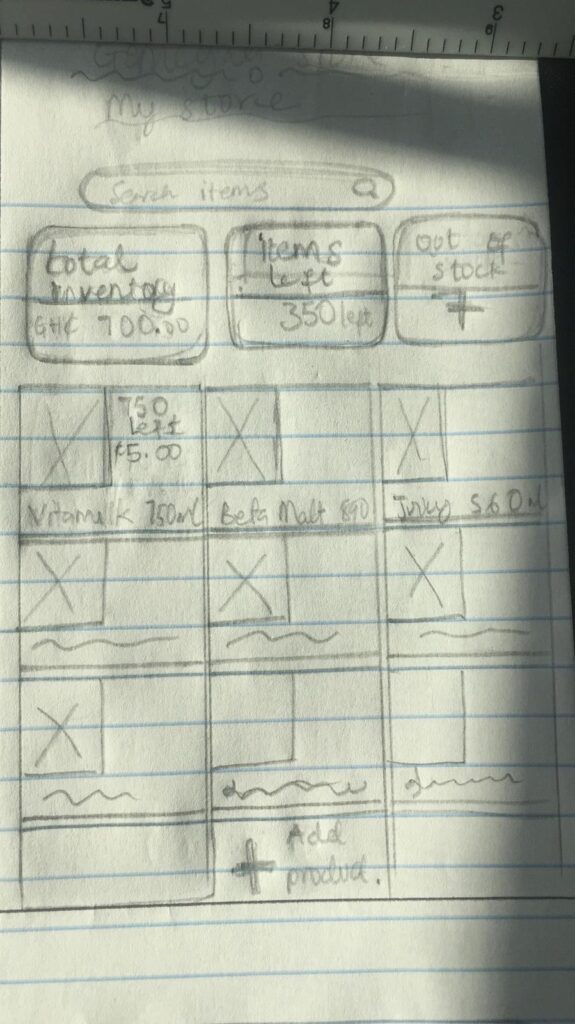
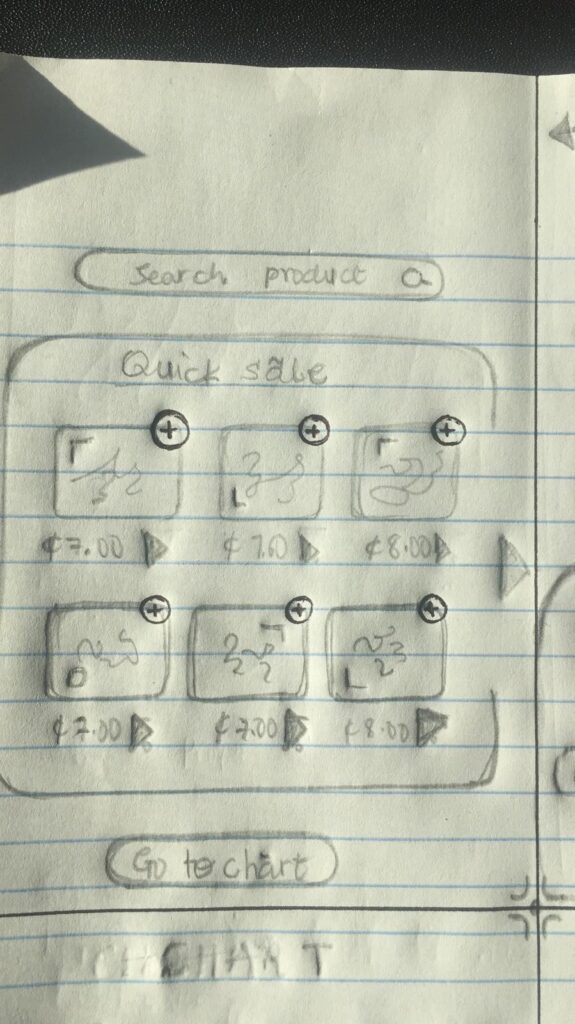
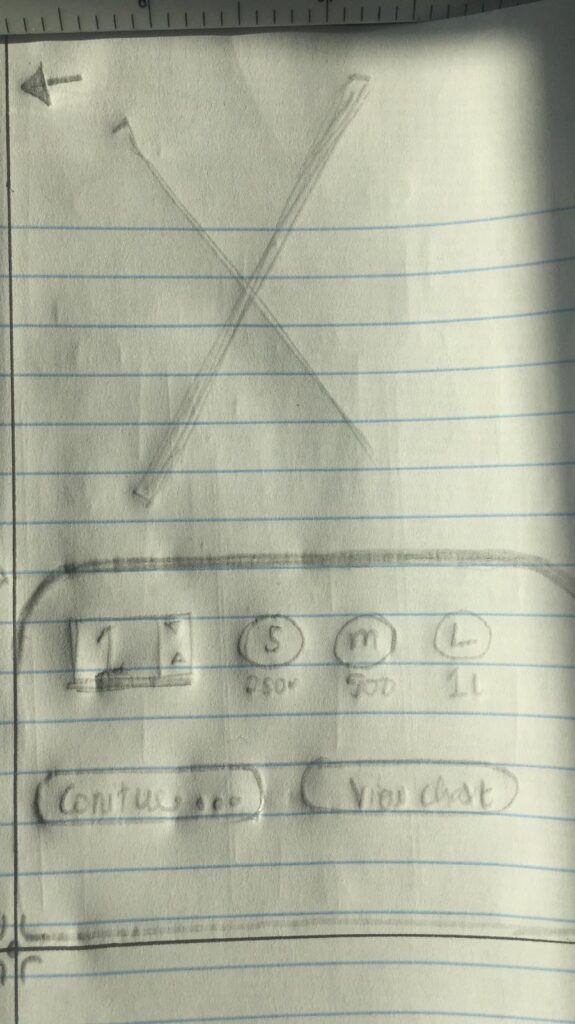

High Fidelity Prototypes
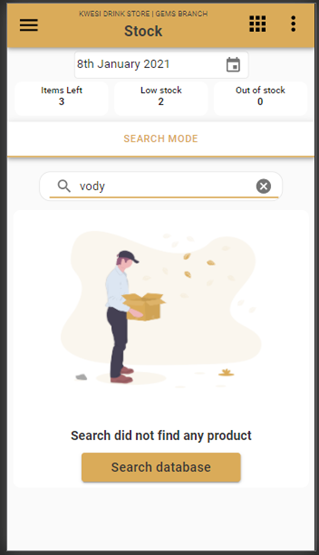

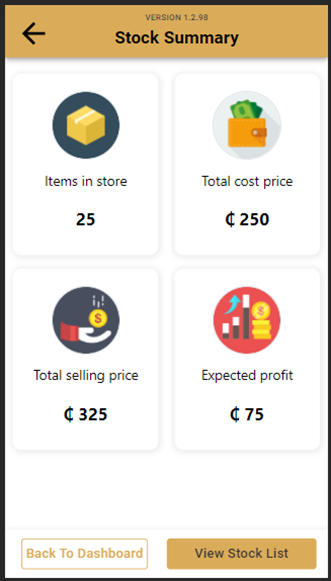
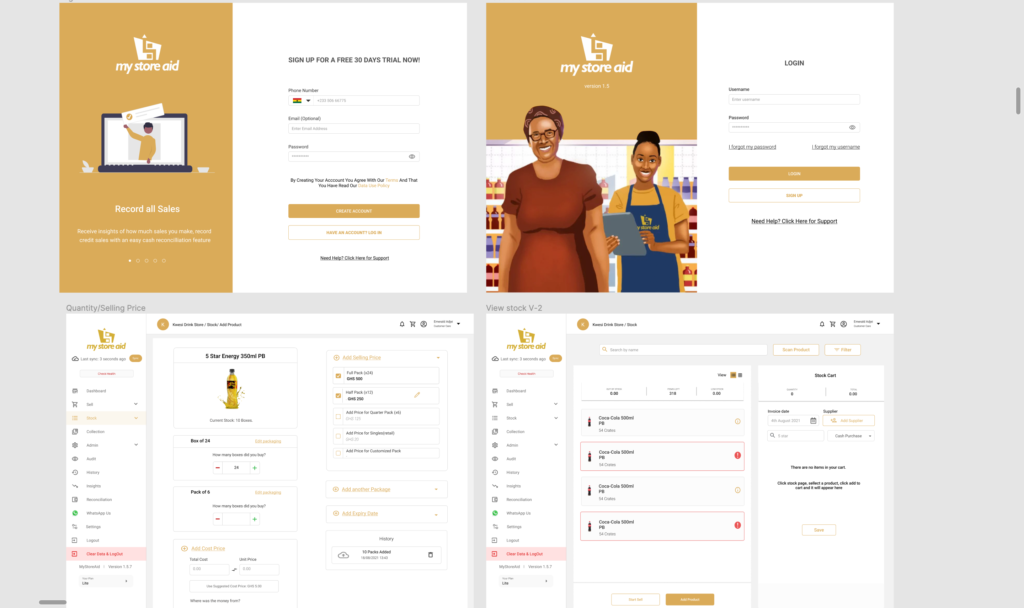
Usability tests
Methods
- Unmoderated usability testing was employed by the design and product team
- A and B testing methods are employed using google sheets
Findings
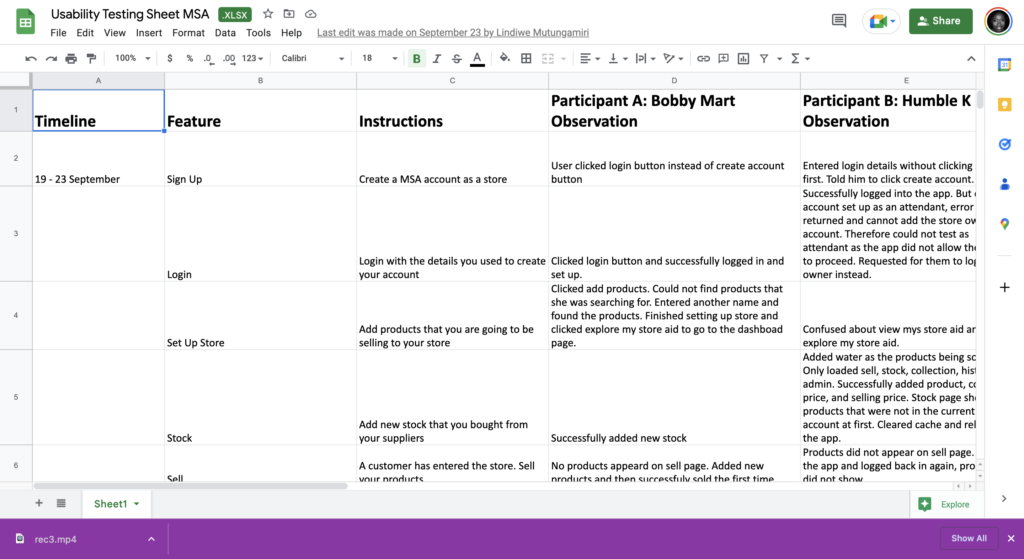
Key Challenges
- Working With Tight Deadlines
- Balance of Design & Function.
- Balance of Client Needs & Personal Design Preferences.
- Staying Relevant & Gaining Skills Constantly.
- Being Unique.
